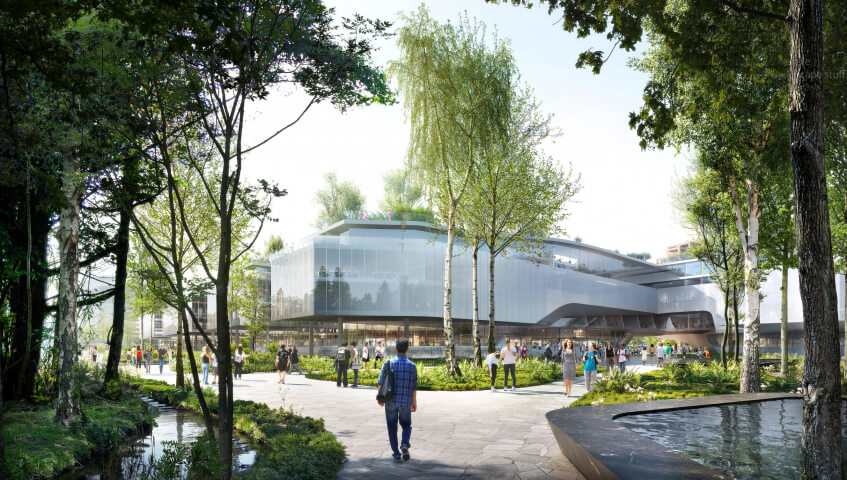
Yangmeikeng Sea Boulevard
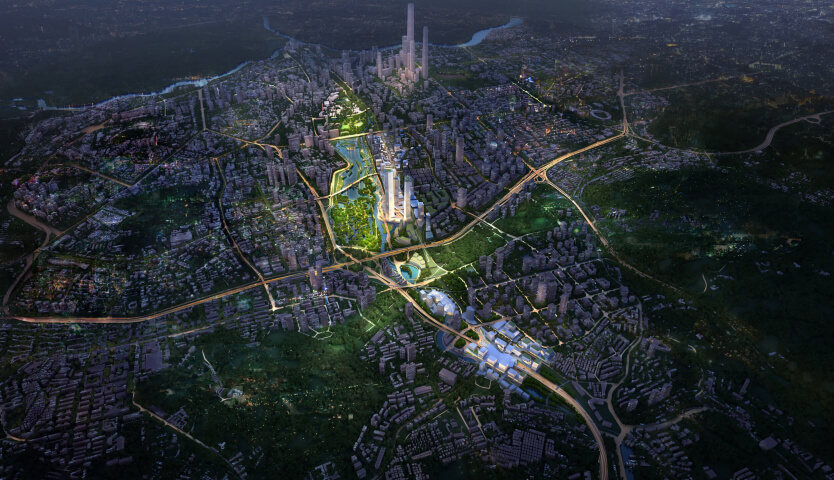
Shenzhen’s Triple Dike coastal defense

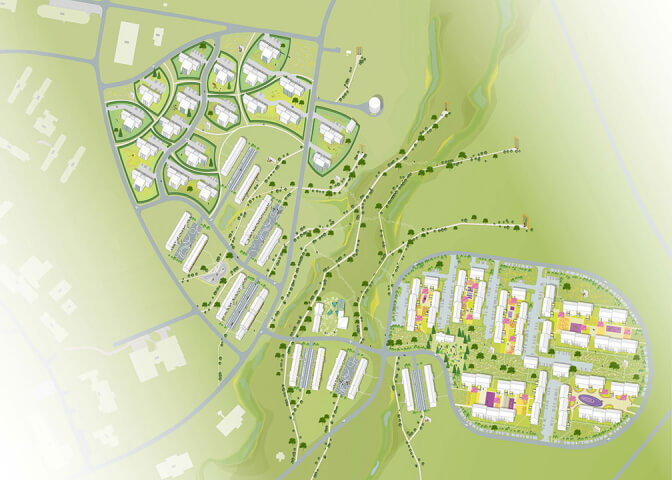
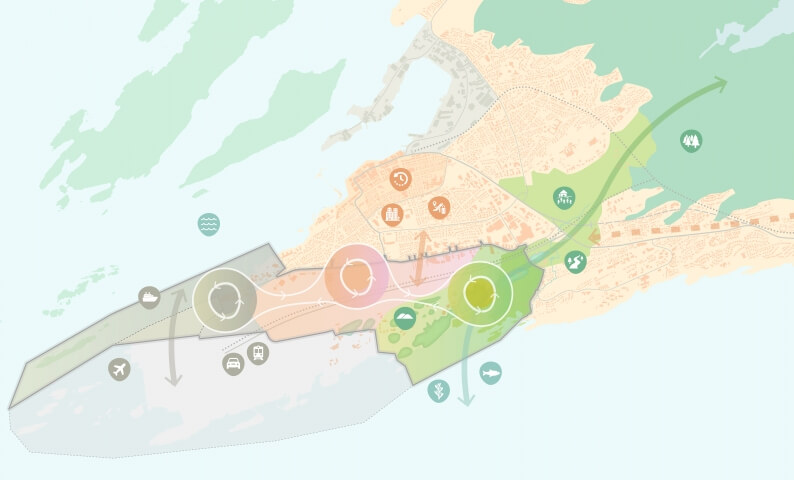
In 2018, the typhoon Mangkhut damaged the coastline of the Dapeng peninsula to various degrees. In 2019, team KCAP+FELIXX was selected to develop plans to restore the coastline and raise protection standards. The team developed the ‘Triple dike strategy’, an integrated approach towards the climate adaptive reorganization of the 130 kilometer long shore. Water safety strategies are connected to eco-development and nature restoration, and merged with social and economic growth.
COASTAL COMMUNITIES
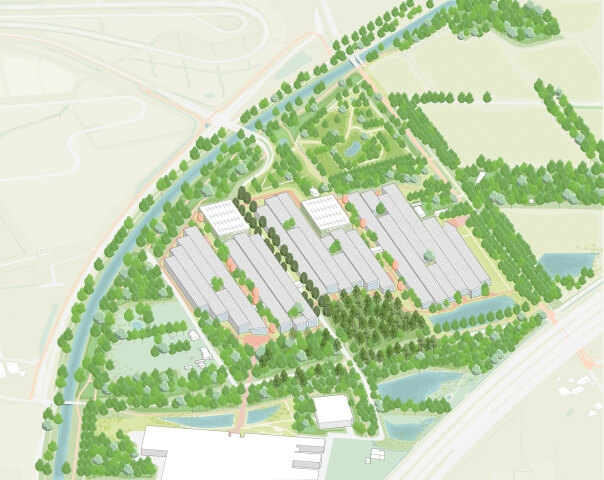
Along the shore, several villages originate from fishing communities. The application of the triple-dike strategy provides these coastal communities with a framework to enhance their existing qualities while unlocking potentials for growth. The small-scale identity of the villages is protected by locating new developments within the existing boundaries. Each village’s specific character is strengthened to amplify the rich variation of recreational facilities.

YANGMEIKENG
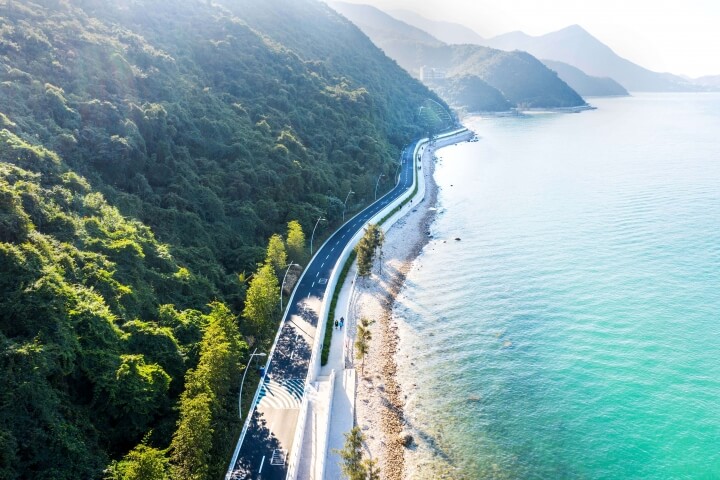
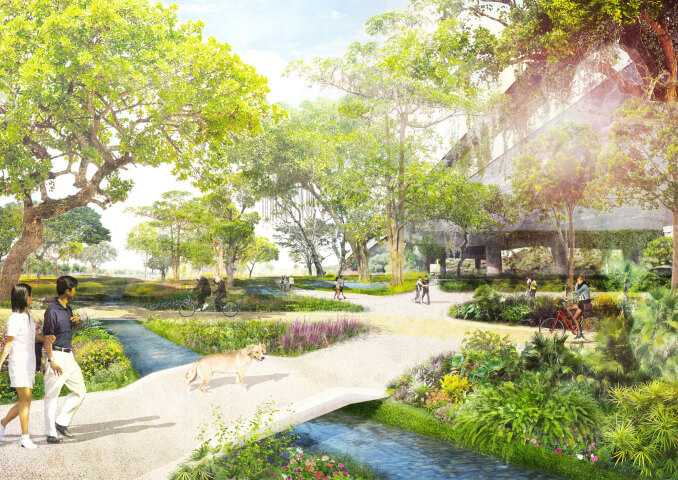
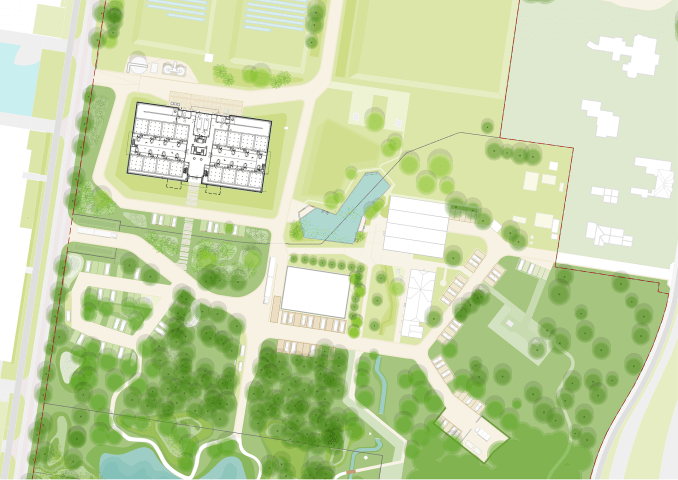
In May 2020 the Yangmeikeng Sea Boulevard was the first of six strategic development areas where the construction of the coastal defense was completed. On a 500m long strip, the performance of proposed nature-based strategies for the sea wall are tested, and materialization principles are explored and refined. The realization of this ‘demonstration zone’ is the first milestone in the construction of 18 kilometers of embankment by 2021.

TRIPLE DIKE
The three protective zones of the ‘Triple Dike’ strengthen the character of Yangmeikeng, as a fortress in the green. The design evades the introduction of a grand metropolitan scale and supports the organic village life. The varied design of the different areas invites users to engage in diverse activities; to go for a swim, have a picnic with friends or take a long walk along the boulevard.

The first protective zone consists of ‘wave-gardens’, mitigating the impact of the flow during storms. They are planted with robust beach vegetation and rocks, and offer places for picnicking, to enjoy the view on the beach.

The middle zone is composed of a sequence of shifting walls, with different heights. They create plazas and sheltered terraces on different levels, connected by a scenic walk.

The third zone is formed by a collection of ‘rain-gardens’, as part of the communal space. The lush vegetation of trees and shrubs blends with the adjacent mountains, and offers covered and shaded places. The gardens collect and infiltrate rainwater and wave overflow.
Walls and pavement blend in with the sand color of the beach. The materialization illustrates the characteristics of the three dike zones: more delicate materials are used for sheltered places, robust and solid elements are used for the exposed zones.

Yangmeikeng Sea Boulevard, before and after photographs
年份
2019 - 2020
位置
Shenzhen, China
类型
整体规划, 基础设施, 景观, 公共空间
规模
42 ha
获奖
2021 Rethinking The Future TF Awards [3rd place]
2021 A+ Awards [winner]
2020 WLA Awards [shortlist]
2020 Eurasia prize [winner]
2019 Competition winner
团队&合作伙伴
Michiel Van Driessche
Marnix Vink
Deborah Lambert
Maria E. Castrillo
Fangfei Liu
Ramona Stiehl
Eduardo Marin Salinas
Klaudio Ruci
Ilva Mishtaku
Natalia Andreeva
Zamira Abazi
Nancy Smolka
Naya Tzika-Kostopoulou
Shuangyun Chen
KCAP
Deltares
Hope Landscape & Architecture
China Water Transport Planning & Design Institute