NBS Catalogue
A Catalogue of Nature-based Solutions for Urban Resilience
More than half of the world's population lives in cities, and that number is rising every day. Urban areas are becoming more crowded, reducing green space and causing loss of biodiversity. Urban environments lose their resilience to mitigate the negative effects of climate change. As a result cities & towns are regularly confronted with devastating floods or heatwaves and droughts that cost millions of dollars in damage and even threaten our livelihoods.
Power of Nature-based Solutions
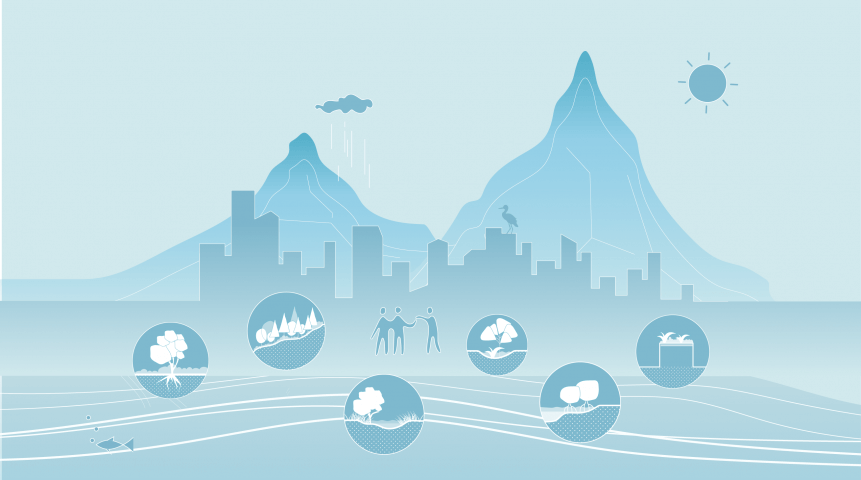
Nature-based Solutions (NBS) are approaches that use nature and natural processes for delivering infrastructure, services, and integrative solutions to meet the rising challenge of urban resilience. NBS can provide multiple benefits to cities and address different societal challenges, including reducing disaster risk and building climate resilience, while also contributing to restore biodiversity, creating opportunities for recreation, improving human health, water and food security, and supporting community wellbeing and livelihoods.

Suitable NBS can be considered dependent on the characteristics of the city such as the hydrological conditions. Different types of cities based on their location in the river basin.
“A Catalogue of Nature Based Solutions for Urban Resilience”
Despite a growing demand for Nature-Based Solutions (NBS) in cities, many people who make planning, financing, and technical decisions for urban resilience have little knowledge of when and how to build with nature. Our NBS catalogue provides them with guidance, real-world examples that illustrate how such approaches have worked, and technical assistance to help identify potentially viable nature-based investments that help cities address resilience challenges.
DOWNLOAD THE CATALOGUE
An integral version of the catalogue can be downloaded from the World Bank’s Open Knowledge Repository
Scalable Approach
Nature-based solutions can be applied across spatial scales and settings in and around cities. Examples include small (local) scale green spaces on buildings; bioswales and green corridors along streets and water bodies; urban parks and forests within city boundaries (city-scale), and larger areas with wetlands and forests upstream or along the coast, sheltering cities from flooding and improving availability and quality of water (regional scale).
slider
Schematic sections of NBS at regional, city and neighborhood scale.
Fourteen Families of NBS
To a degree, the position of a city determines the suitability of NBS types. To help select appropriate NBS the catalogue contains fourteen NBS categories. Urban Forests, Terraces and Slopes, River and Stream Renaturation, Building Solutions, Open Green Spaces, Green Corridors, Urban Farming, Bioretention Areas, Natural Inland Wetlands, Constructed Inland Wetlands, River Floodplains, Mangrove Forests, Salt Marshes, and Sandy Shores. We call these the NBS families.

The fourteen NBS typologies – so called ‘NBS Families’.
Structure of the Catalogue
 Section: Processes of NBS-Family "Urban Forest"
Section: Processes of NBS-Family "Urban Forest"
Richly visualized the catalogue describes and assesses each of the NBS approaches based on the following criteria:
- Processes- relevant for the resilience, functions and benefits of NBS, including infiltration, cooling and carbon sequestration.
- Functions - volumetric/quantitative capacity to regulate the effects of potential natural hazards.
- Benefits - capacity of NBS to deliver social, economic, and environmental benefits, such as reduction of flood, heat stress risk, human health improvement, job creation and biodiversity enhancement.
- Suitability - environmental, technical and urban requirements for implementation as well as information on maintenance and costs.
- NBS practice - key examples (worldwide) with relevant lessons learned on social, financial aspects and considerations of governance.

Diagrams: Functions and Benefits (for people) of NBS-Family "Urban Forest"
Collaboration
“A Catalogue of Nature-Based Solutions for Urban Resilience” was made for the World Bank Group and Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery (GFDRR). The Catalogue was developed together with the World Bank team in collaboration with Nelen & Schuurmans, UNStudio, Rebel and UNSense.
The Catalogue of Nature-based Solutions for Urban Resilience has been developed as a guidance document to support the growing demand for NBS by enabling an initial identification of potential investments in nature-based solutions. The Catalogue intends to support policy makers, project developers, development professionals, urban planners and engineers with the identification of potential NBS investments, and to start a policy dialogue on NBS in cities. The structure of the NBS catalogue and focus on application and practice of NBS families underlines the importance of moving NBS from the theoretical discussions towards actual (and global) implementation.
 Axo: Three techniques for NBS-Family "Urban Forest": Phytoremediation forest, Ecological forest corridors & Agroforestry
Axo: Three techniques for NBS-Family "Urban Forest": Phytoremediation forest, Ecological forest corridors & Agroforestry
Year
2020 - 2021
Type
Research, Infrastructure, Landscape
Client
World Bank Group
GFDRR - Global Facility for Disaster Reduction and Recovery
Publications
A Catalogue of NBS for Urban Resilience - World Bank
Biind
Architecten Web
Openbareruimte.nu
Rooilijn
Team & partners
Michiel Van Driessche
Eduardo Marin Salinas
Nadya Nilina
Cherk Ga Leung
Zofia Krzykawska
Elan Redekop van der Meulen
World Bank
Nelen & Schuurmans
UNStudio
Rebel
UNSense