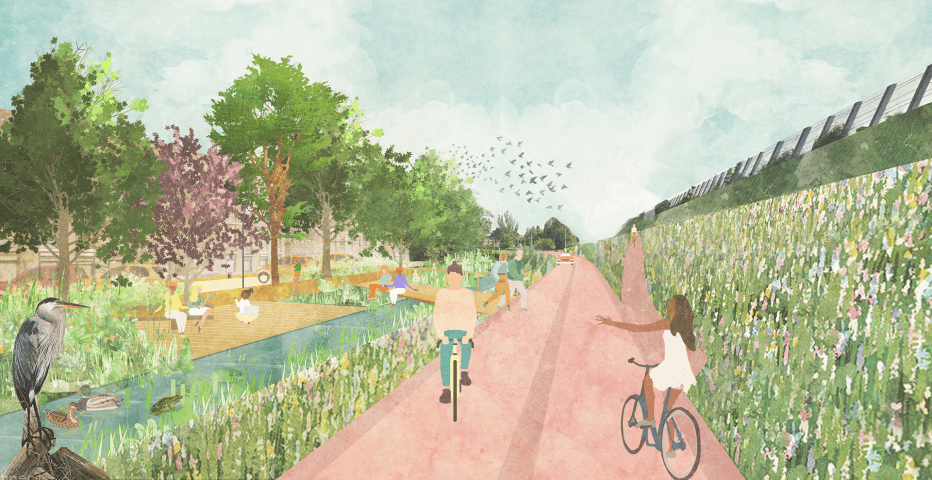Socio-technical city of the future
An urban vision for the Central Innovation District
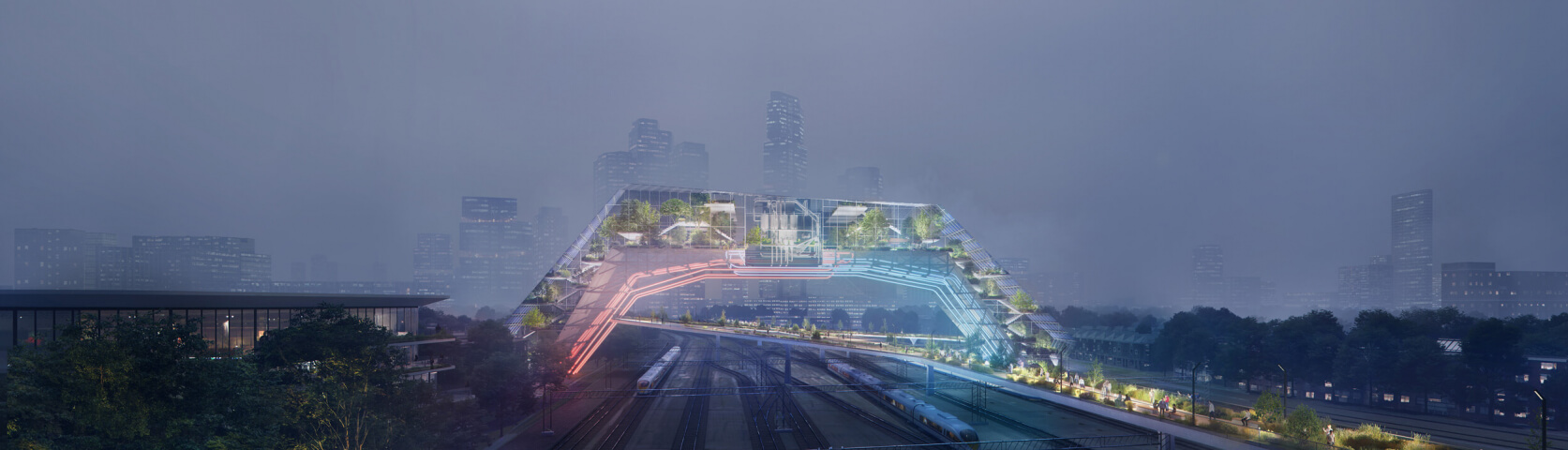
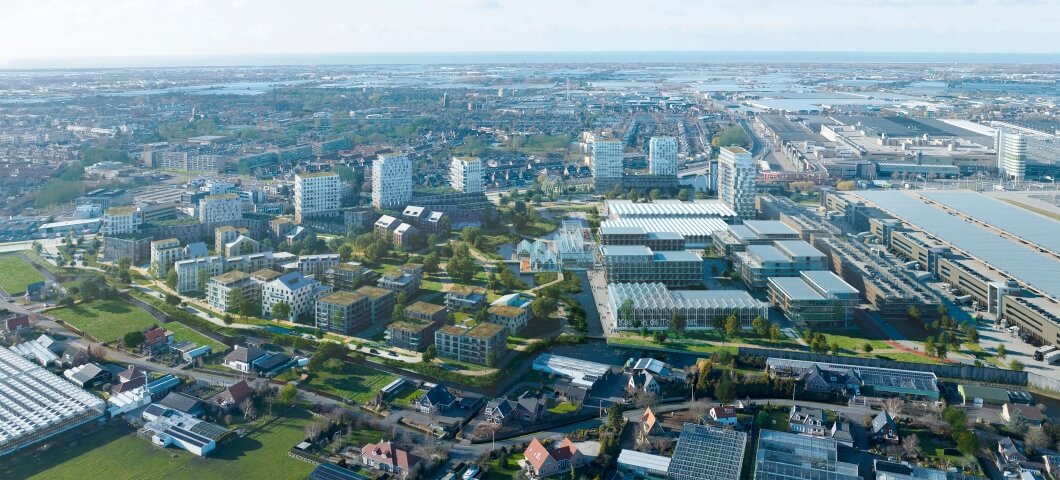
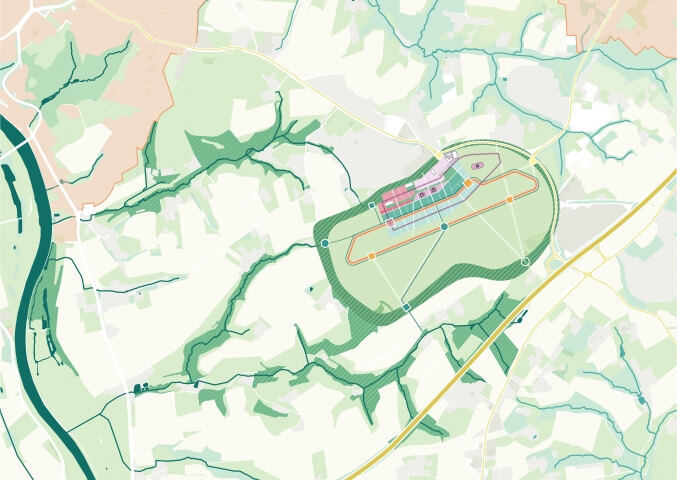
Felixx joined UNStudio in the development of The Socio-Technical City, a new urban vision for the 'Central Innovation District' (CID) square kilometer test site in The Hague. Currently the CID is a major infrastructure hub within the triangle of the Hague Central Station and two nearby stations, but in the future vision of the Socio-Technical City it becomes a green, self-sufficient double-layered district, where a new urban layer of housing, offices, urban mobility and park-like public space is composed over the existing train track infrastructure.

The City of the Future
How can the major social transitions taking place in the fields of energy, food and mobility be realized in our cities in a way that is both future-proof and attractive? This is the question that underlies the design vision of the Socio-Technical City. Our vision for The Hague is one of the studies made for 'The City of the Future', a joint initiative by BNA Research (the Royal Institute of Dutch Architects), the Delft University of Technology, the Delta Metropolis Association, the municipalities of Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, Utrecht and Eindhoven, the Directorates-General for Mobility and Transport, the Environment and Water, the Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management and the Ministry of Interior.
The project started in January 2018, when 10 multidisciplinary design teams were tasked with investigating new ways of city-making using five test locations in Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague, Utrecht and Eindhoven. These teams included landscape architects, urban planners, mobility experts, experts in the field of circular economy, energy transition, future strategies, big data, smart cities etc. The teams worked on a level playing field together with municipalities, stakeholders and experts in the field of important innovations.

Socio-Technical City: a response to key transition issues for the future
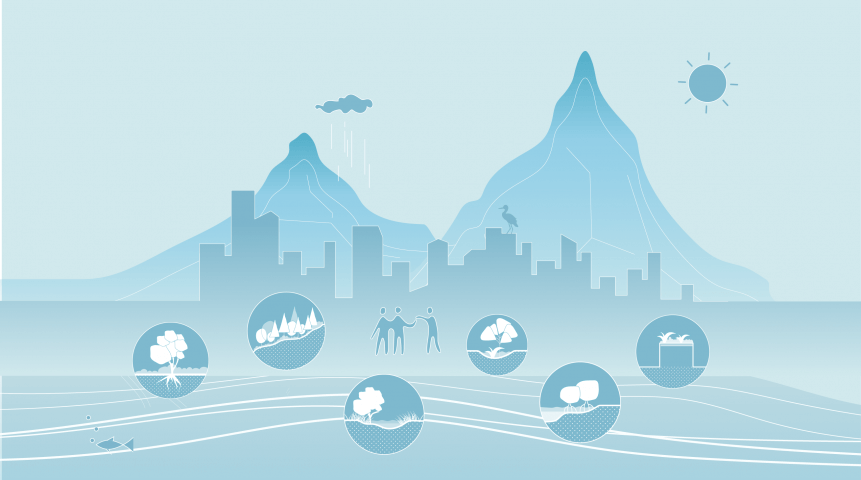
Our concept for the Socio-Technical City combines the two largest challenges facing the future of cities - urbanisation and sustainability - and focuses specifically on the questions: how can an area like the CID, despite extremely high density in the future, be self-sufficient and energy-neutral? What does such an urban district look like? And how can you connect the technology that is required with the people who live and work there?

Gateways: Catalysts for encounter and innovation
With the elevated urban layer covering the existing railway tracks, our urban vision distinguishes a number of technical 'domains', which refer to the major transition issues of our time: energy, circularity, mobility, climate adaptation / water management and food production. These domains are then each envisioned as 'gateways': physical architectural interventions that offer practical solutions to the problems as well as functioning as attractive symbols for the specific themes - a geothermal power station as an icon for energy transition, a (Hyperloop) station as a landmark for mobility, a Biopolus water treatment plant as a symbol for circularity. In this way, the Socio-Technical City bridges the gap between infrastructure and technology on the one hand, and quality of life and social well-being on the other.

The model of the gateways is based on the idea that interaction is a requirement for innovation. The gateways form catalysts for meeting; they connect neighbourhoods and people and thus form breeding grounds for innovation.

Gateway Mobility: the Metropolitan Superhub
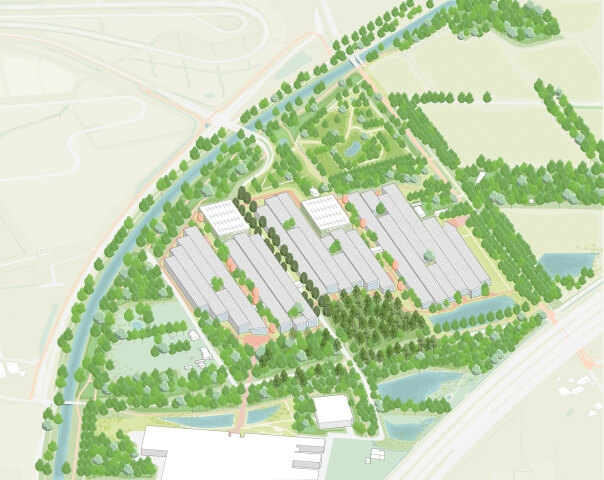
The concept for the gateways is inspired by the location itself. The existence of three intercity stations within walking distance of each other presents an unprecedented opportunity to transform this area into one Metropolitan Superhub; a system of closely linked terminals, comparable in size to Amsterdam Schiphol Airport. It also provides an opportunity to create space for new forms of sustainable mobility such as the Hyperloop, with a free floating system of electric scooters, and possibly self-driving pods, interlinking the different modes of public transport.
Following the construction of the elevated urban layer, the Metropolitan Superhub can gradually become a city centre. The city grows all around it and connects to this layer, while creating a level of density that is unprecedented in the Netherlands.

Gateway Geothermal Energy Plant: an energy cathedral, city bridge, winter garden and co-working space for start-ups
The geothermal energy plant is the central location of the energy supply and as such is an important gateway for the CID. Research shows that the use of heat pumps, Heat & Cold storage systems, optimum insulation and solar panels are not enough to fully supply a compact area such as this. In order to make the district self-sufficient and energy-neutral, a solution was found by way of a system of 'energy exchange' with the surrounding districts. The geothermal energy plant draws energy from a hot water reservoir that is 2.5 kilometers below ground and supplies it to the surrounding low-rise districts. In return, the low-rise districts generate a surplus of energy via roof-mounted solar panels that can be delivered to the new high-rise buildings.

The energy gateway is not only a geothermal power plant, but also a bridge that connects neighbourhoods, a winter garden and co-working space for start-ups. But above all it is a symbol for energy transition: an energy cathedral.
Gateway the Biopolus: urban irrigation system with wadis, water squares, canals and waterfalls
In Socio-Technical City the Biopolus forms another gateway, a circular system that provides local food and water supplies. The Biopolus ensures that the waste water from the new part of the city is purified and the nutrients that are released are used for the cultivation of crops. Waste water is pumped through tubes to the highest level, after which it flows to the lowest level via various purification processes, producing drinking quality water which then enters the system again. The localised cycle is complete.

The Biopolus is however not merely a water purification plant, it is also an urban farm, a vertical park and an emblem of the circular economy.

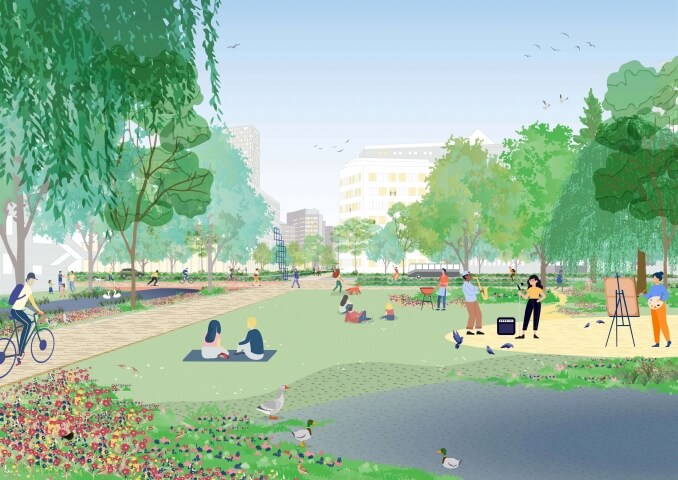
Gateway Climate Adaptation: Water plazas
Climate change presents significant risk factors for the area, such as flooding and overheating. Where currently rainwater, waste water and grey water are all disposed of through one drainage system, in the Socio-Technical City this is separated into different systems. Waste water is drained through underground pipes, however the relatively clean rain water is re-used and made visible in the form of water features in public spaces: an irrigation system of canals, water plazas and waterfalls.
All images ©UNStudio
Year
2018
Location
The Hague, The Netherlands
Type
Research
Client
BNA Research
Delft University of Technology
Delta Metropolis Association
Municipality of The Hague
Team & partners
Michiel Van Driessche
Marnix Vink
Deborah Lambert
Steven Broekhof
Iris van der Walle
UNStudio
UNSense
DGMR
Metabolic
Nelen Schuurmans
Here technologies
Renders by Plomp