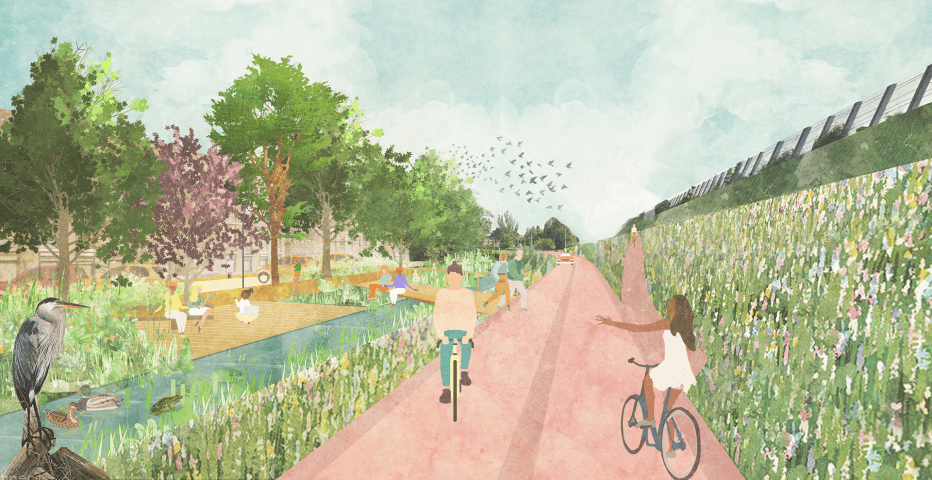Towards a healthy city by foot
The Journey approach
The Dutch Board of Government Advisors & Felixx Landscape Architects and Planners investigated the potential role of walking in contemporary urban environments.

Walking has great potential. It may not be the fastest, and as some may say not the most comfortable way to get around, but it is the only type of movement which doesn't require a vehicle. By walking more, we limit the influence of our movements on the environment. As a result, creating room for walking frees up space in the city, which can be used to tackle diverse social and environmental challenges. Oddly enough, the pedestrian is often forgotten in the design of our public spaces. This research by design is developed in close collaboration with urban psychologist Sander van der Ham – STIPO. It provides insight into the potential benefits of walking, and identifies the design tasks within our built environment to realize these benefits.
Walking as a choice
Walking is a choice, although we often do not make that choice very consciously. In order to create environments that encourage people to walk more, we need to understand how we can influence people’s choice to do so. The choice of walking is influenced by many factors. Everything we experience in the course of our lives is stored in our brain as information. We roughly have two methods or "systems" to interpret this information, and make choices based on it.

System 1 makes unconscious, emotional, fast, automatic, and effortless decisions. Choices are based on rules of thumb that originate from previously acquired knowledge, experiences or emotions. They undergo little to no critical reflection. System 2 is rational and requires conscious reflection and costs a lot of energy. It allows informed choices to be made, and questions the rules of thumb of system 1. To boost walking, we need to address both systems in our way of designing cities.
The Journey approach
Space for walking is often designed according to the same "mechanical" logic as that of roadways. The experience en route is secondary to reaching the destination as quickly as possible. This constantly confirms the prejudices of system 1 in our brain: you are faster by car or by bicycle.

Reconnecting society with walking, after years of applying generic rules of car environments, starts by applying human-oriented measures to our streets and public space.



Walkable spaces based on enhancement of comfort, proximity, and rewarding can bring humanized street designs that subconsciously tempt us to choose to walk.
Walking as agenda catalyst
By placing walking in a broader context, we can make better informed conscious decisions. By critically reflecting on our current rules of thumb and habits, walking can become a more obvious choice over time. We can achieve this by linking the act of walking to the contribution it makes to social and environmental agendas.

This makes the choice for walking more than a mere choice of mobility. It becomes a conscious choice for less air pollution and a cleaner and healthier world. By associating walking with different challenges and objectives, we create arguments that can encourage us to walk and transcend the practical consideration of going somewhere by foot. The more diverse the links, the wider the audience that will feel compelled to walk.




The walkable city
The 20th century was without a doubt the century of the automobile. Mass production of cars had revolutionized mobility and represented a milestone in the democratization of transport. The pursuit of speed and individual freedom has led to a spatial layout which follows the logic of the car. This legacy is still visible in our urban environment today. Cities are still largely organized to get from A to B as quickly and efficiently as possible.

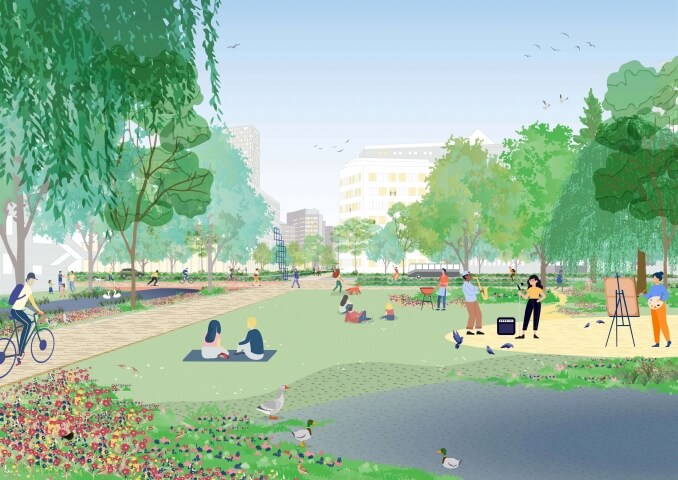
The research proposes a method to transform an infrastructure network into a functional experiential landscape. A walkable city where the journey is as important as the destination, recognizes local streets, green-blue networks, neighborhood services and amenities, schools, urban plazas, and public transport stations as the structural elements for a walking operational journey, rather than limiting the walking realm to sidewalks parallel to car infrastructure.
In a timeframe of changing mobility, walking can act as a catalyst to realize various governmental agendas. Strategies for, for example, climate adaptation, emission reduction, safety, densification and population growth can be linked in the space that is freed up by the increase of walking. But this link also comes with a requirement in return. The experience of the city must entice residents and visitors to walk. In this city human scale is normative, physical activity is stimulated and space for social interaction is created. A walkable city shares a design brief with that of a sustainable and healthy city.
A brief story about walking
slider
Rotterdam as a showcase
To investigate the feasibility of the walkable city, the research takes Rotterdam as a testcase. The city is an interesting study area because of the dominant role the car has played in the design of the city. After the bombing of the city center, the "Basic Plan for the Reconstruction of Rotterdam" was developed. The devastated area was swept clean, creating the opportunity to build a completely new street pattern according to modernist principles. Living and working areas were separated, and space was created for the "traffic of the future". Four test locations were selected, to test the transformation from a car-oriented layout, to a walkable city.

Four test locations were selected based on the positions about the city center and the spatial design of the district. These are four urban prototypical compositions made in the Netherlands common, making the research relevant and applicable to other locations. We analyze the urban environment based on criteria that people use in their decision to walk: proximity, comfort, and rewarding to identify the main points for the three criteria in the area and investigate how they can be improved while keeping an eye on the specific conditions of the place. Besides it, we identify other social challenges for which walking can be a solution and we examine how walking can effectively and visibly make a positive contribution to these challenges in the area.
Case 1: Urban renewal districts - Nieuwe Westen

Case 2: Post-war neighborhoods - Ommoord

Case 3: Residential district - Hoogvliet

Case 4: Business park - Spaanse polder

Year
2019 - 2020
Location
The Netherlands
Type
Research
Client
College van Rijksadviseurs
Awards
2021 WLA Award [winner]
Publications
download document
Ruimte voor lopen
Architectenweb
Gooood
Mooool
Omgevingsweb
Stadszaken
UrbanNext
Team & partners
Michiel van Driessche
Marnix Vink
Deborah Lambert
Eduardo Marin Salinas
Elan Redekop van der Meulen
Cherk Ga Leung
Sander van der Ham